Three New KDT Projects for the Department of Electrical Engineering, boosted by CPSe
The Department of Electrical Engineering at TU/e again had a good year in relation to the KDT2022 calls. Thanks to the project acquisition support of CPSe, the department was awarded three prestigious KDT proposals (calls KDT 2022). In the subsequent sections, we present a comprehensive overview of each of these projects and the PIs who are involved in them.
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](https://assets.w3.tue.nl/w/fileadmin/_processed_/6/b/csm_RPODID_682ef6b1fb.jpg)
R-PODID: – HORIZON-KDT-JU-2022-2-RIA - 2 PhDs
Title: Reliable Powerdown for Industrial Drives
Aims: R-PODID will develop an automated, cloudless, short-term fault-prediction for electric drives, power modules, and power devices, that can be integrated into power converters. Thereby, electrical and mechanical faults of machines and of the power converters driving them will become predictable within a limited prediction horizon of 12-24h. This will enable a power-saving shutdown of a larger number of production machines during idle times, because a looming failure during the next power-on cycle can be reliably foreseen. It will also enable reliable mitigation of dangerous faults in applications using modern power-devices like silicon-carbide (SiC) and III/V-semiconductor devices like gallium-nitride (GaN).
TU/e role: Fault modelling for Electro-Magnetic Compatibility and Power Quality is relevant to enable adequate and sustainable protection against disturbance emissions in an installation. These emissions impact the on-going delivery of services and are harmful for the long-term electro-mechanical reliability of electrical drives.
The R-PODID sensors enable the collection of datasets beyond the state of the art and a multidisciplinary behavioral analysis of electromagnetic emission generated by power devices and electric drives in fault mode will be made. AI- algorithm will be developed and optimized on resource-sparse microcontrollers to handle electromagnetic emission changes and input impedance changes caused by animalities in operation over the complete frequency range (50Hz – 30MHz).
Staff involved: Anne Roc’h
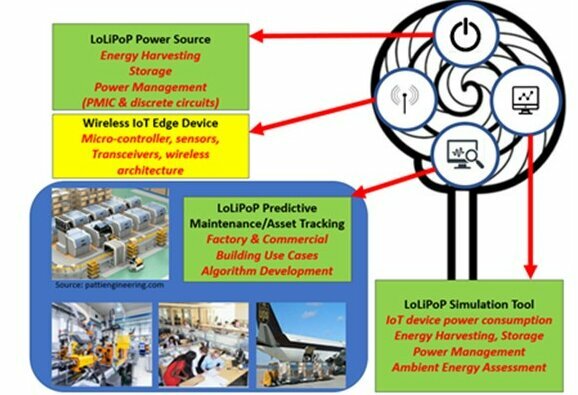
LoLiPoP: – HORIZON-KDT-JU-2022-2-RIA – 4 PhD positions (2 for EES, 1 for SPS and 1 for IE&IS)
Title: IoT innovative Long Life Power Platforms
Aim: LoLiPoP will enable retrofitting of wireless sensor network (WSN) modules in IoT applications. This includes the development of algorithms to perform functionalities like asset tracking and condition monitoring (for predictive maintenance). They can be used in applications such as industry 4.0, smart mobility and energy efficient buildings. LoLiPoP IoT creates an ecosystem of developers, integrators and users to develop these platforms thinking about power/battery life, ease of installation and maintenance. The project is driven by 12 laboratory- and field-based use cases to initially demonstrate their technical viability and then potential impact. Expected impacts from the LoLiPoP IoT use cases include; a) typical battery life increase from ~18 months to >5 years, b) Reduced maintenance overhead of mobile and fixed assets from >30% to <15%, c) Reduced costs related to location of assets typ. by €100Ks PA per use case, d) Optimised flow, management and throughput of assets through the identification of bottlenecks, yielding reductions of >10% in production time, cycle time and inventory costs, e) Improved comfort levels and well-being of building occupants whilst reducing energy footprint by >20% and f) Revenues of >€10M PA for LoLiPoP IoT industry partners offering asset tracking & condition monitoring services. All of this is achieved by developing and integrating: a) Multi-source Energy Harvesting solutions (vibrational and photovoltaic transducers, PMICs and discrete circuits), b) Digital interfacing to contextually adapt mode settings of WSN devices and connected systems to minimise power drain, c) Ultra low power components for WSN, d) Innovative Architectures for wireless data collection that minimize battery power drain, e) Simulation Models to optimise component design and integration and f) embedded AI/ML in IoT devices, for lower latency and power consumption and higher robustness.
TU/e role: TU/e-EE will supervise 3 PhDs and IE&IS will supervise 1 PhD together with BE.
EES with its 2 PhDs will develop novel over the air test methodologies for testing WSN and will use passive radar techniques for monitoring people movements inside smart building whereas SPS with its PhD will use of measured WSN data to track human activity/factors and build adaptive intelligence in a smart lighting system, based on well-being and perception constraints measured by a PhD at IE&IS and BE.
Staff involved: Ramiro Serra, Jean-Paul Linnartz, Ingrid Heynderickx.
EcoMobility: KDT-JU-2022-2-RIA-Topic-1 HORIZON - 1 PhD, 1PostDoc
Title: Intelligent, Safe and secure connected Electrical Mobility solutions: Towards European Green Deal and Seamless Mobility
Aim: EcoMobility will support European industry and cities in transitioning from isolated and static transportation means towards a service centric, connected mobility ecosystem by sharing data and services across involved stakeholders. The project will enable and simplify cooperative development, deployment, operation and life cycle management of connected adaptive end-to-end mobility solutions in a sustainable manner.
EcoMobility will:
- establish devops practices within the supply chain with continuous and customized cloud-based addition and improvement of mobility services,
- support contract-based runtime coupling of mobility services within edge/cloud-based service for deployment of AI solutions, coupled with monitoring, analysis and coordination of vehicles, transportation infrastructures and people,
- deliver reliable & enhanced vision, perception, including HD maps, and localization systems for safe, connected, and automated vehicles,
- deliver customized and improved fail-operational ADAS systems reflecting technology capabilities of heterogeneous vehicles and protecting vulnerable road users,
- provide energy-aware control and scheduling of electric vehicles including smart Battery Management Systems (BMS) and coordination with other transportation means,
- contribute to increased public acceptance of electrified autonomous vehicles and bridge gaps between technological advancements and legal and regulatory frameworks.
The demonstrators within EcoMobility will showcase the project’s findings and capabilities for the end-to-end sustainable mobility ecosystem with impact on improved trust, safety, security, efficiency and ecology of mobility solutions to a level appropriate for mass-market deployment. Emerging innovations will leverage the expertise of world-renowned industrial and research partners within the mobility value chain, giving Europe a competitive edge in a growing market with direct contributions to the European goal of zero road fatalities by 2050.
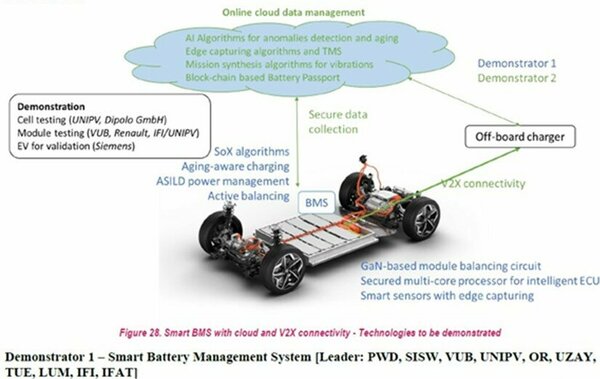
TU/e role: Electromechanics and Power Electronics (EPE) group in TU/e will develop a connected smart battery management system with cloud-based Artificial Intelligent (AI) services and enhanced hardware capabilities for increased battery lifetime and reliability. How: Model-based and AI-based BMS incl. SoX estimation, charging, balancing and anomaly fault detection
Expected key impact: Lifespan extension thanks to a better battery management which consequently reduces the environmental impact and the cost.
Staff involved: Steven Wilkins, Esin IIhan Caarls