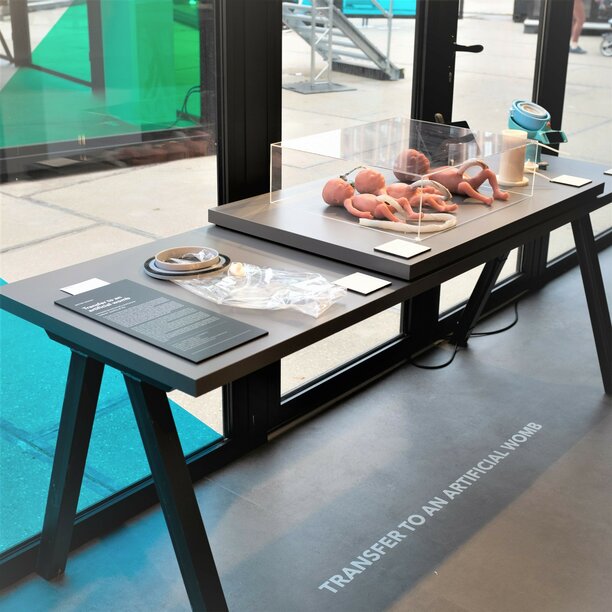
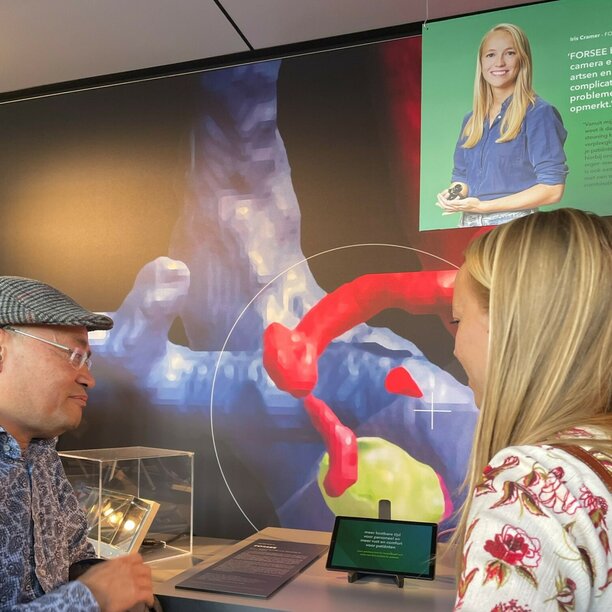
Four e/MTIC projects at Dutch Design Week 2022
During the 2022 Dutch Design week 22-30 October, four major e/MTIC projects were on display at various locations. At Strijp-S -Ketelhuisplein, the TU/e Drivers of Change exhibition presented the projects FORSEE, Perinatal Life Support (PLS) and ACACIA. In the Klokgebouw at the Embassy of Health section, you could find the Pregnancy Risk Flagging System (PRFS) as part of the MEDUSA project. An even more extensive presentation of the ACACIA (Improving cancer care with human-centred AI) project was displayed at the Philips Museum.
PICTURES DDW22
To get an impression of the Dutch Design Week 2022 and the participating e/MTIC projects, we created a small photo album were you can find some informal pictures of this wonderful and exiting event.