Artificial Intelligence in the Built Environment
Our built environment has a huge impact on all aspects of our lives, not in the least quality of life and climate change. As an effect, huge potential resides in digitizing this industry and making data available for intelligent management and optimization of our environment (acoustic performance checking, sensor-based building management, IoT-enabled construction sites, etc.). Various Artificial Intelligence techniques are investigated and adopted in the department of the Built Environment and used for improving the quality of our built environment.
Research Themes
Ambient Intelligence
Ambient Intelligence is receiving much attention for realizing smart buildings and smart cities where sensors and algorithms are incorporated in the environment to optimize processes in real-time ranging from in-door climate control to public transport services.
Digital Twins of buildings and urban areas
Digital Twins of buildings and urban areas are of use for monitoring and improving operational buildings (HVAC, lighting, solar shading, etc), construction sites (feedback loop with construction site equipment), and for urban flow monitoring (people, goods, traffic).
Prediction
Prediction has always been of major importance in the built environment, particularly for facilitating informed decision-making in the design and engineering phases. Machine Learning techniques are increasingly adopted to predict behavior of buildings, urban areas and their use (flow monitoring).
Robotics
Robotics are of increasing importance to construction sites, manufacturing plants, cities and operational buildings, thus transforming the built environment in a semi-automated environment with high-tech robotics in all its aspects.
Energy Transition
A huge shift in energy use is needed for the built environment. Switching from the use of natural gas to renewable heating sources relies heavily on AI algorithms (prediction, learning, monitoring) and devices (ambient intelligence, edge AI).
Related research groups:


Urban Mobility
In order to improve urban mobility, an increasing number of personal information systems and decision support systems are built and used, relying on advanced visualization techniques (VR, AR), digital twins of people in the environment, and machine learning algorithms for prediction and providing personalized advice.
Related research groups:
Reference projects
Machine Learning and sensor data
Based on various machine learning algorithms including Bayesian belief networks and decision trees, an integrated data analytics tool is developed to generate the spatial and temporal information related to travel and activities. By Tao Feng
Self-adaptive personal information systems
A Bayesian method for incremental learning an individual’s preferences based on his or her choice behavior is developed and applied in personal travel information systems. By Theo Arentze
Digital Twins and Linked Building Data
Web-based information systems are developed, which collect various sorts of data about a building in a decentralized manner, including detailed 3D object models, point clouds, image data, semantic data, sensor data. By Pieter Pauwels
AI in manufacturing
Manufacturing of complex geometries (parametric and structurally optimized structures with minimal material use) will be enabled by digital manufacturing techniques, e.g. robotics in construction and additive manufacturing. By Rob Wolfs
House as Robot
By developing extreme scenarios and building mock-up’s, we aim to evolve everyday living spaces to adaptive living organisms that understand and empathize with the user. By Masi Mohammadi
SWT and Linked Data in Autonomous Mobility
Using ideas behind Linked Data and Semantic Web, allows the AI in charge of handling Autonomous Vehicles to consume valuable information from the surrounding ecosystem in order to achieve more optimal calculation of control parameters of the vehicle while using minimal amount of network resources. By Milos Viktorovic
Automated fault detection of photovoltaic (PV) systems
Large-scale monitoring of distributed PV systems in comparison with expected PV output generated by a digital twin network, taking into account dynamic weather conditions, partial shading due to urban surroundings (e.g. from LiDAR data) and the non-linear characteristics of inverters and power systems. By Roel Loonen
Expert systems for spatial-structural-physics design generation
The built environment is responsible for about 40% of the worldwide energy and material resources, and housing demands are growing, due to an increase of population, and become more complex. This requires fully optimized renovated and new buildings, and, of utmost importance, also optimized design processes: the products and their conceptualization need to be revolutionized. An open source available C++ toolbox has been developed, which provides super structured and super structure free spatial design representations; expert systems to generate, modify, and assess discipline specific representations; and data analysis and visualization tools. By Hèrm Hofmeyer
Healthy Working and Living Environments
With increasing pressure in our daily work and life, it is difficult to maintain a healthy balance and healthy environment to live in (air quality, acoustics, ambiance, and so forth). Sensing our environment and adjusting it to our individual and common needs requires AI techniques (ambient intelligence, digital twins, prediction).
Related research groups:


Smart Cities and Buildings
The built environment, both on a building and urban scale, is heavily embedded with devices, sensors, and actuators. As a result, the environment is made artificially intelligent, and it actively responds to its users (interactive ambient intelligence).
Related research groups:
Staff
Nitant Upasani
Soora Rasouli
Aiyu Zhu
Jelle Versteeghe
Tao Feng
Herm Hofmeyer
Ekatarina Petrova
Olivia Guerra Santin
Roel Loonen
Melvin Wong
Davide Leonetti
Theo Arentze
Theo Salet
Masi Mohammadi
Dujuan Yang
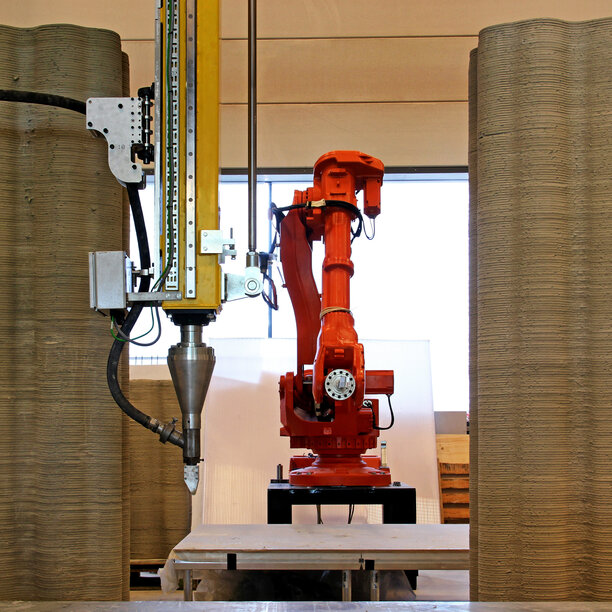
Industry 4.0 in Construction
Construction sites and manufacturing for construction is heavily digitized and automated (digital twins, robotics). Autonomous robots are increasingly incorporated in factories and construction tasks, improving the productivity of the construction industry.
Related research groups:
- Robotics, Automation, and Manufacturing
- Information Systems in the Built Environment
- Building Services
- Applied Mechanics

Autonomous Vehicles
Urban mobility is shifting heavily, from a more traditional car- and pedestrian centered mobility, into a dense network of various kinds of transportation means. Autonomous vehicles are expected to invade the city fabric and interact with a network of devices (IoT) for a range of daily tasks.
Related research groups: